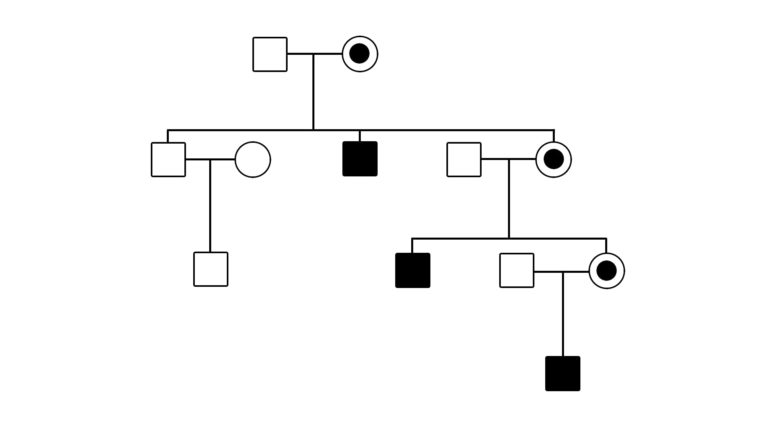
Home / Healthcare & Medicine / Biology & Biotechnology / The Genomics Era: the Future of Genetics in Medicine / X-linked recessive inheritance
This article is from the free online
The Genomics Era: the Future of Genetics in Medicine


Reach your personal and professional goals
Unlock access to hundreds of expert online courses and degrees from top universities and educators to gain accredited qualifications and professional CV-building certificates.
Join over 18 million learners to launch, switch or build upon your career, all at your own pace, across a wide range of topic areas.