What Are the Health Effects Related to Shift Work?
 The rhythm of the body is complex © Colourbox
The rhythm of the body is complex © Colourbox
There are thousands of publications on shift work and possible impacts on health. The conclusions of many of the publications in the field are sometimes contradictory and / or ambiguous, and it can be difficult to use the results in practice. The reasons why it is difficult to investigate this topic are numerous, but one important factor is that people are different! Genetic differences can be very significant. Some tolerate night work without problem, while others definitely do not.
The human circadian rhythm and the homeostasis
If you want to understand the effects from shift work on health, it is useful to understand some things about the human circadian rhythm. “Circadian” comes from Latin, and means approximately one day. The circadian rhythm of a person is believed to be about 24 hours, but may vary from person to person (from 22 to 25 hours). The term circadian bodily functions are often used to describe those bodily functions that are most active during the day and which reduce their activity at night. Examples include: Body temperature, heart rate, blood pressure and metabolism. Theories about the health effects of shift work have often been focused on changes in the circadian body functions. If a person starts to be awake at night and sleep during the day, it takes about seven days before the body is able to “reverse” body functions to be most active at night. This is why it might be difficult to sleep at daytime. Your body clock does not agree to this situation, the body is set to being awake! This is a mechanism, which exists in addition to a mechanism we call homeostatic; which here means that we have a certain specific need for sleep. Even if you manage to sleep enough hours, your body will still not be adapted to a different circadian rhythm before some days have passed. So – you need perhaps seven hours of sleep. After a night shift you may sleep seven hours during the day after. If you start another night shift afterwards, you will still be tired in the middle of the night, as your body clock – the circadian rhythm – wants you to go to bed and sleep instead of being awake. The disturbance in the rhythm explains some of the negative health effects due to night shift work.
Sleep disorders
Sleep disorders are common when working night shifts © Colourbox
Night shift workers often sleep 1/3 less time per day than they usually do during periods of such work. Day sleep is different from night sleep both regarding length and quality. The sleep during a night can be divided in different types of sleep, for instance deep sleep and sleep with dreams; when we can observe that the sleeping person has “Rapid Eye Movements” (REM). Most night shift workers have less REM sleep and less deep sleep than usual. It is possible that this may lead to the following complaints:
- Constant feeling of being tired / exhausted
- Sleep problems
- Mental irritability
- Depression
Sleep problems can be a fairly immediate reaction to shift work, and is probably the reason why many choose not to start this kind of work.
Indigestion
Several studies show that indigestion is common among people with irregular working hours. It appears that such problems develop after some time, for instance after a period of some years of shift work, and the resulting changing daily rhythms. The health problems are described both as an increased incidence of symptoms of stomach / intestines, and increased incidence of diseases such as gastritis, ulcers and irritable colon. These problems arise presumably because digestion follows the circadian rhythm although people are awake and eat at night. Also, the eating habits may become irregular when working night shifts.
Cardiovascular disease
There are studies suggesting an increased incidence of cardiovascular diseases among workers with irregular work hours. However, it is difficult to distinguish the effect of type of work and the effects of other important factors, such as smoking, for example. Smoking tobacco is a known to increase the risk of developing cardiovascular disease. It is therefore possible that the increased incidence of cardiovascular diseases within the group shift workers is related to a combination of these factors. The shift work itself may play a role, but the shift work also seems to be associated with more smoking. During the night shift, a smoker may have higher tobacco consumption than during daytime. This illustrates how difficult it is to provide reliable conclusions from studies of shift workersand for finding the cause of development of diseases. Another factor of importance is the gender; the increased risk of cardiovascular disease related to shift work is seen most clearly in men. After menopause in women (~50 years), the gender difference seems to disappear. This might indicate that hormones may be a part of the mechanism for developing this type of health problems.
Cancer
It has been shown that women who have worked night shifts for many years, are at increased risk for breast cancer. This risk seems to develop after a period of more than ten years of night shift work, and this has been found among nurses who work night shifts only, not those with other forms of shift work. This issue is debated, some find this an important issue to consider, others do not believe this information is true.
Reproduction
Some studies show that women are at increased risk for miscarriages if they work night shifts. It is most likely that this applies to women who work permanent night shifts on a regular basis, not those working in rotating shift schedules. It is not clear if this problem is related to any hormonal changes caused by the shift work, or if there are other factors on the night shifts that may cause the spontaneous abortions. Sometimes night shift workers are few, and they must work harder than during the day shift.
Injuries and accidents
 Errors at work may occur more during night shifts than during daytime © Colourbox
Errors at work may occur more during night shifts than during daytime © Colourbox
There are numerous studies of shift work and accidents. Night work may increase the incidence of both injuries and accidents. This is best seen from studies in hospitals, the number of errors and mistreatments of patients increases at night. Many studies from industry show, strangely enough, that night work does not provide any increased incidence of injuries. It can be interpreted in light of the many activities that actually stop during the night, the risk of accidents and injuries is reduced. Many of these studies, however, have been conducted by the industry itself, or been paid by the industry – and one can discuss if this connection between industry and researchers may have influenced the results. Economic considerations are strong when deciding whether work should be done around the clock – or not.
 Chernobyl nuclear power plant © Colourbox
Chernobyl nuclear power plant © Colourbox
Several tragic accidents have been associated with lack of sleep and shift work. This photo is from the Chernobyl nuclear power plant in Ukraine, which exploded in 1986, one of the worst nuclear disasters in the world. It has been reported that the engineers involved had been at work for 13 hours or more.
Consequences for family life and social activities
Shift workers have often time off when others have not, and are sleeping or at work when others have their leisure hours. This may cause social isolation of the shift workers, and reduce the time available for family and friends. This can cause problems, which could have an impact on health. Increased incidence of mental symptoms, family problems and drug abuse has been suggested to be related to shift work.
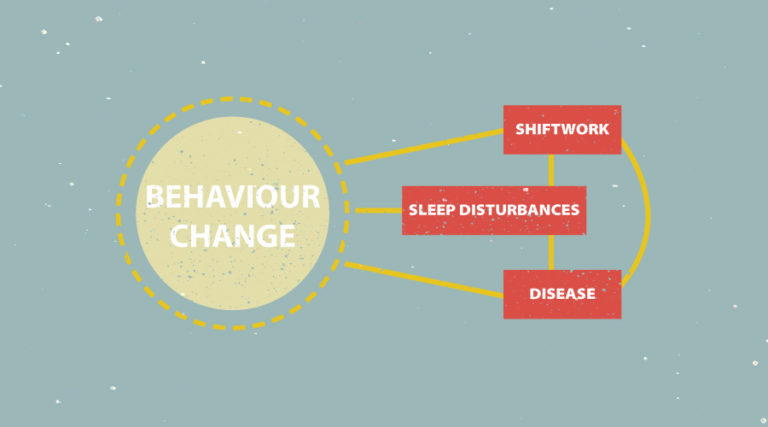 This figure illustrates the complexity related to shift work and health. The shift work itself may cause diseases. However, in addition, the shift work may lead to behavior changes (such as increased smoking or less contact with other persons) which also can have negative health effects. Sleep disorders is a part of it all. © University of Bergen
This figure illustrates the complexity related to shift work and health. The shift work itself may cause diseases. However, in addition, the shift work may lead to behavior changes (such as increased smoking or less contact with other persons) which also can have negative health effects. Sleep disorders is a part of it all. © University of Bergen
Share this
Occupational Health in Developing Countries

Occupational Health in Developing Countries


Reach your personal and professional goals
Unlock access to hundreds of expert online courses and degrees from top universities and educators to gain accredited qualifications and professional CV-building certificates.
Join over 18 million learners to launch, switch or build upon your career, all at your own pace, across a wide range of topic areas.
Register to receive updates
-
Create an account to receive our newsletter, course recommendations and promotions.
Register for free







