Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality in the Food Industry
In this article Alberto Dávalos introduces virtual reality and augmented reality and how it can contribute to personalised nutrition and consumer engagement.
What is augmented reality?
Augmented reality is an enhanced version of reality where live direct or indirect views of physical realworld environments are augmented with superimposed computer-generated images over a user’s view of the real-world, thus enhancing one’s current perception of reality. No special equipment is needed. The only integral accessory is the smartphone; and requirements is geolocation. Applications include: medical training, design and modeling, tourism industry, classroom education, business logistics, entertainment properties.
What is virtual reality
Virtual reality is an artificial environment which is experienced through sensory stimuli (such as sights and sounds) provided by a computer and in which one’s actions partially determine what happens in the environment. Virtual reality glasses is the equipment needed and a PC with support is also required, Applications include: military, education, healthcare, entertainment, fashion, business, engineering and digital marketing.
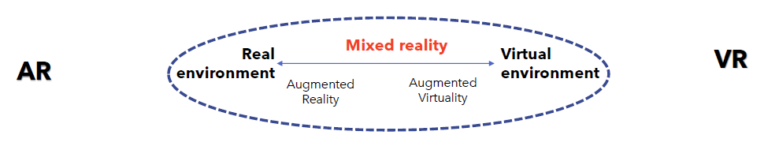
Augmented reality vs Virtual Reality
Table 1: Augmented Reality vs Virtual Reality
| Augmented Reality | Virtual Reality |
|---|---|
| Images are created using applications that mixes virtual content and real life content together | Creation of an actual world, not just some contents of it |
| Users are able to distinguish between the two | Hypothetically, users cannot tell the difference between what is virtual and what is real |
| No augmented headset is required | Some sort of virtual reality headset is required |
| Users remain in the real world | Users are “transported” into a new world |
| Challenges include: limited visual field by the size of the display; handling can result in tired arms; poor availability of glasses; multitude of different providers , specific apps or programs and a big market that needs to be centralised; and privacy | Challenges include moving beyond gamers to target a broad market; high cost of production; uncomfortable and no portable headset; isolation os users; and cyber sickness |
Figure 1: Augmented Reality vs Virtual Reality
Applications of AR and VR to Personalised Nutrition
- Calculation of portion size: Until today, it has been difficult to calculate self-motivated food energy / nutrient analysis in real life. This is because the ordinary food image does not have a dimensional reference, preventing the size of the food from being gauged.; and the two-dimensional image lacks information about the three-dimensional surface of the food which defines its volume. Augumented reality and virtual reality can help in volume estimation required for accurate nutrition.
- Increase the satiety: Modifying percpetion of satiety and controlling nutritional intake by changing the apparent size of food with augmented reality.
- Treating eating disorders and obesity: Virtual reality is a useful technology for enhancing traditional cognitive-orientated therapies, helping to address body image dissatisfaction, increasing self-esteem and self efficay.
Applications of AR and VR in Consumer Engagement
What consumers are looking for currently is a totally different level of engagement with the product. The engagement with the brand, with the company, with the product is a crucial point of consideration for the modern customer. Augmented reality as a digital marketing tool is something that can give much more immersive experience for the customer, mostly in terms of advertising. As most of the commerce goes online, one of the most popular features of augmented reality among consumers is the visualization of the products, which makes purchasing experience much easier and less obscure. (Charlesworth, 2018).
1. Digitial Food:
Augmented reality filters can
- Create new flavours and food experiences
- Contribute to the reduction of waste by playing with food digitally
- Allow ordering of food, e.g. You can directly order Domino’s pizza using a Snapchat filter
2. Food packaging
Traditionally, food packaging was used to protect the food against deteriorative effects of the external environment; communicate with the consumer as a marketing tool; enable easier usage of products; and contain products of various sizes and shapes. Augmented reality in food packaging can add a virtual element to packaging. Thus helping to:
- Improve brand loyalty and attract more customers
- Stand alone from competitiors
- Extend a businesses real estate
- Increase product visualization
- Avoid repackage if it needs an update
- Increase brand engagement
3. Equip people with cooking skills
Augmented reality and virtual reality can help a food business in getting and retaining customers. For example, using real photographs as references for 3D models. It can provide a virtual assistant to help with the learning of cooking skills; and personalized instructional materials.
4. Food Safety
Agumented relaity and virtual reality can:
- Allow the creation of a detailed visual world for employees to learn the task needed. In turn, this can increase efficiency of employee training, shortening the learning curve, and saving material and human resources. It can also be used to
- Eliminate errors in food processing
- Food traceability
- New efficiencies to warehousing and pick-and-pack
- Apps to determine food composition and degree of maturation
- Apps to idenitfy food fraud
5. Marketing in customer’s experience
The technology allows experiences to share in social networks, spreading the word through social media marketing and entertainment at the table.
6. Adding interactivity to products
- Apps to identify energy content of the plate after taking a picture
- Overlaying additional information, visual stimulus and interaction on top of specific items give product companies the chance to combine the digitial world with the physical one in a targeted and seamless way (e.g. the use of filters on platforms such as Instagram and Pinterest)
- Engagement of customers to the products is required for more exposure and thus leading to higher sales. The aim is to interact with customers digitially to attract attention of potential and returning customers.
7. Sensory Science
- Sensory evaluation to understand how humans perceive and respond to the various stimuli in food using the fives senses of sight, smell, touch, taste and hearing. This can help in the evaluation of acceptability and competitiveness of food products.
- Digitial technology provides a new era of consumer connectivity and thus, a new technique available for capture and decither consumer’s sensory perception
In Summary
To conclude, virtual reality and augmented reality will not replace human beings in the food industry trades, but are designed to assist people in their work and everyday tasks. Bearing in mind that the system of augmented reality is still in development, but with huge potentials this solution has shown that the future of product tracking can be expected int his area too.
Share this
Revolutionising the Food Chain with Technology

Revolutionising the Food Chain with Technology


Reach your personal and professional goals
Unlock access to hundreds of expert online courses and degrees from top universities and educators to gain accredited qualifications and professional CV-building certificates.
Join over 18 million learners to launch, switch or build upon your career, all at your own pace, across a wide range of topic areas.
Register to receive updates
-
Create an account to receive our newsletter, course recommendations and promotions.
Register for free